Setup OS Requirements RHEL¶
This section describes how to perform the setup for Red Hat Linux Server 7.4. The Peek platform is designed to run on Linux.
Please read through all of the documentation before commencing the installation procedure.
Installation Objective¶
This Installation Guide contains specific Red Hat Linux Server 7.4 operating system requirements for the configuring of synerty-peek.
Required Software¶
Some of the software to be installed requires internet access. For offline installation some steps are required to be installed on another online server for the files to be packaged and transferred to the offline server.
Below is a list of all the required software:
- Python 3.6.x
- Postgres 10.4.x
Optional Software¶
- Oracle 12c Client
Installing Oracle Libraries is required if you intend on installing the peek agent. Instruction for installing the Oracle Libraries are in the Online Installation Guide.
- FreeTDS
FreeTDS is an open source driver for the TDS protocol, this is the protocol used to talk to the MSSQL SQLServer database.
Installation Guide¶
Follow the remaining section in this document to prepare your RHEL operating system for to run the Peek Platform.
The instructions on this page don’t install the peek platform, that’s done later.
Install Red Hat Linux Server 7.4 OS¶
This section installs the Red Hat Linux Server 7.4 64bit operating system.
Create VM¶
Create a new virtual machine with the following specifications
- 2 CPUs
- 4gb of ram
- 50gb of disk space
Install OS¶
Download the RHEL ISO
Mount the ISO in the virtual machine and start the virtual machine.
Run through the installer manually, do not let your virtual machine software perform a wizard or express install.
Staring Off¶
At the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4 installer boot menu screen, select:
Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4
At the language selection screen, select:
English
Goto SOFTWARE SELECTION screen, select Minimal Install or Server with GUI if you’d like a GUI.
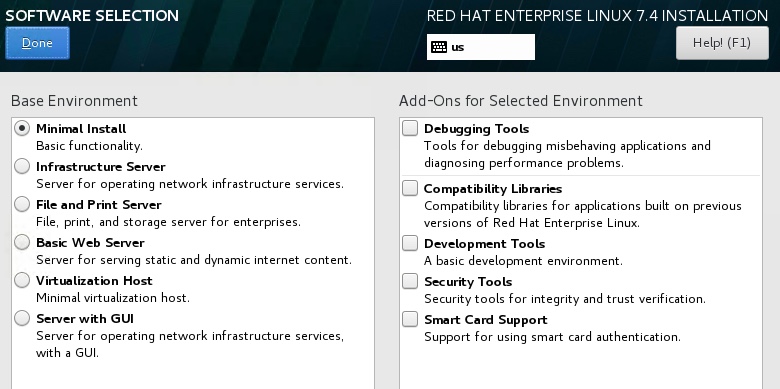
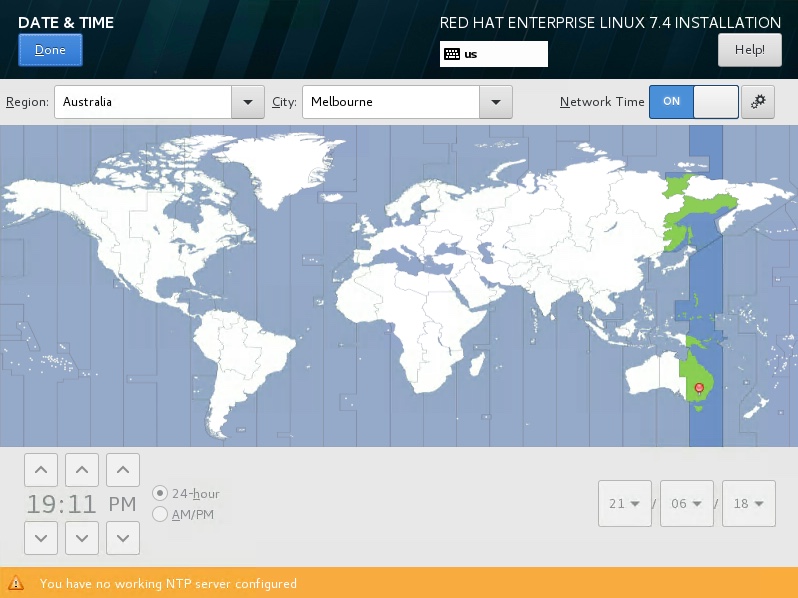
Goto DATE & TIME screen, select the appropriate time location.
Goto KEYBOARD screen, select the appropriate keyboard, or leave as default.
Goto NETWORK & HOST NAME screen,
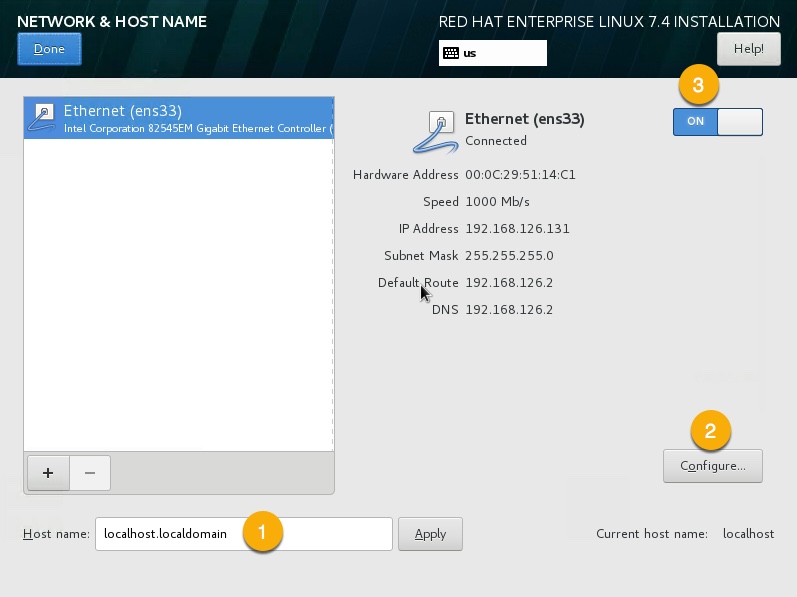
enter your desired hostname or:
peekconfigure IP address,
Configure IP address:
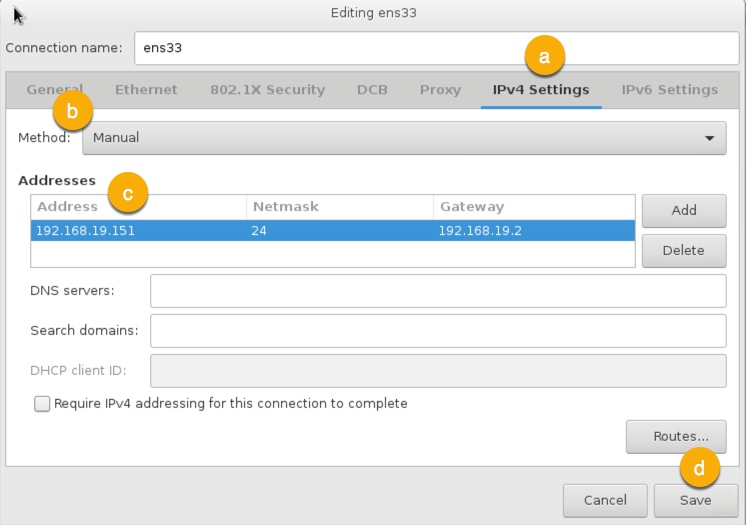
- Goto IPv4 Settings tab,
- Set Method to Manual,
- Add static IP address,
- Save.
enable network.
Goto INSTALLATION DESTINATION screen,
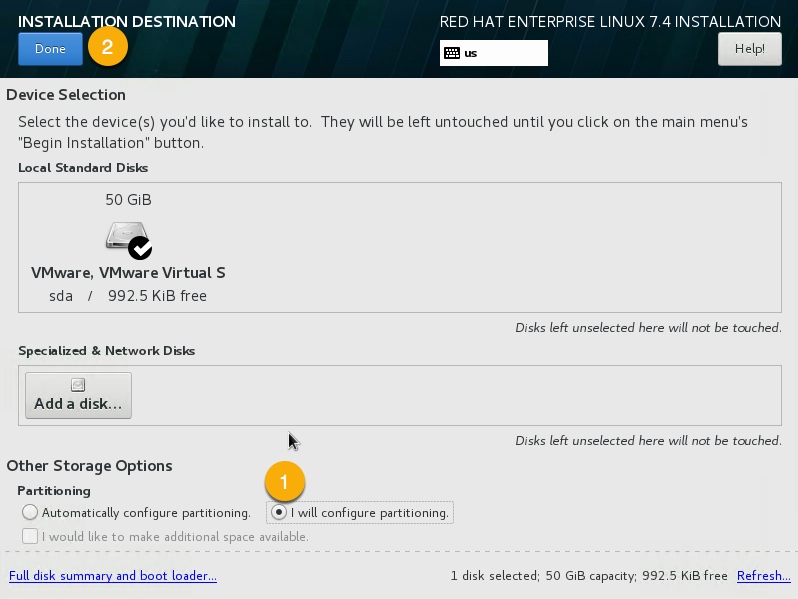
for partitioning select:
I will configure partitioning.
Select Done.
Partition Table¶
We’ll be creating three partitions, /boot, / and swap. For a heavily used production server you may want to create more virtual disks and separate out /var, /home, and /tmp. With one file system per disk.
Having one file system per disk removes the need for the overhead of LVM, and the VM software can still expand the disk and filesystem as required.
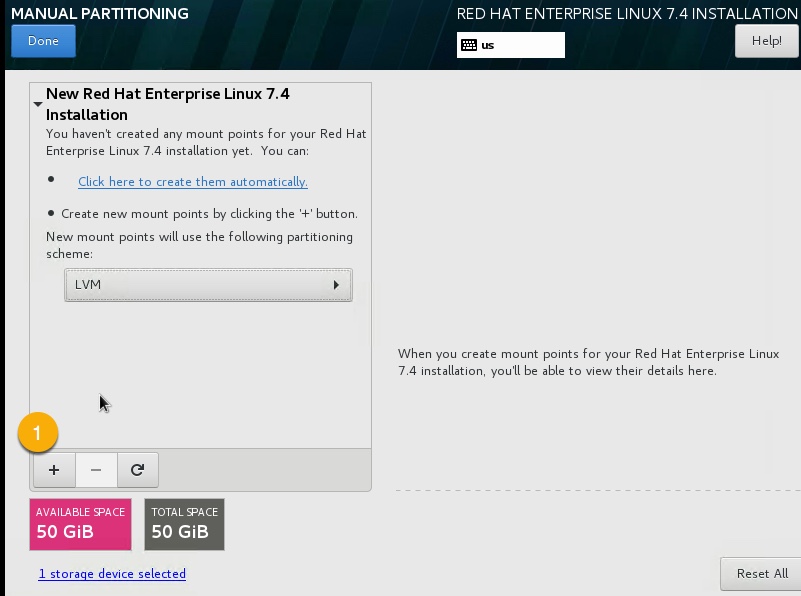
- Add partition,
repeat for each partition.
/boot¶
Select the following disk from the ADD NEW MOUNT POINT menu:
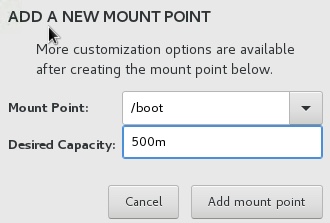
Mount Point:
/boot
Desired Capacity:
500m
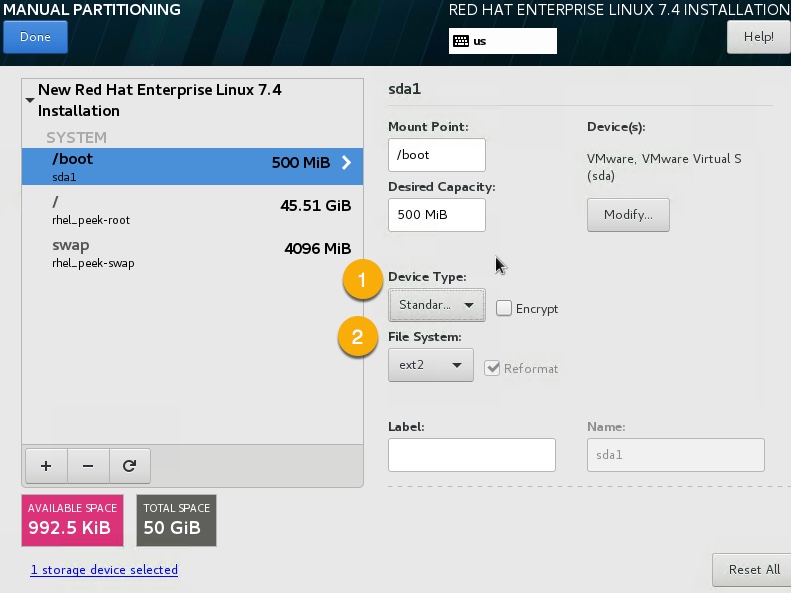
- Set Device Type to standard,
- Set File System to ext2.
swap¶
Select the following disk from the ADD NEW MOUNT POINT menu:
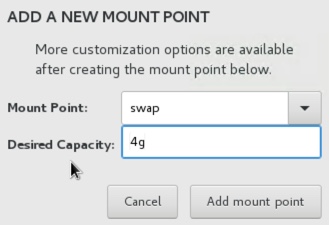
Mount Point:
swap
Desired Capacity:
4g
/ (root)¶
Select the following disk from the ADD NEW MOUNT POINT menu:
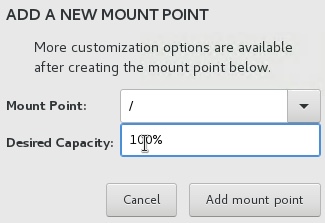
Mount Point:
/
Desired Capacity:
100%
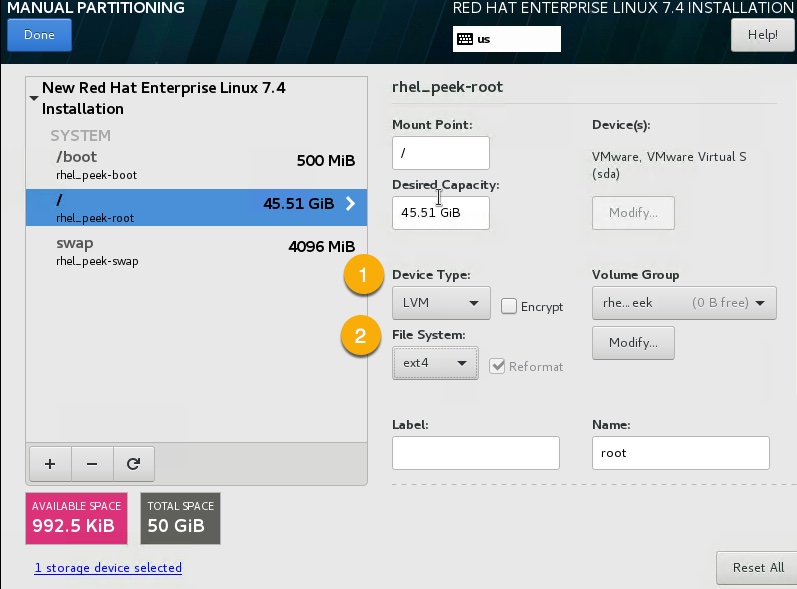
- Set Device Type to LVM,
- Set File System to ext4.
Select DONE review the SUMMARY OF CHANGES
BEGIN INSTALLATION
While Red Hat is installing you can configure the USER SETTINGS, set ROOT PASSWORD and go to the USER CREATION screen.

Create the peek user.
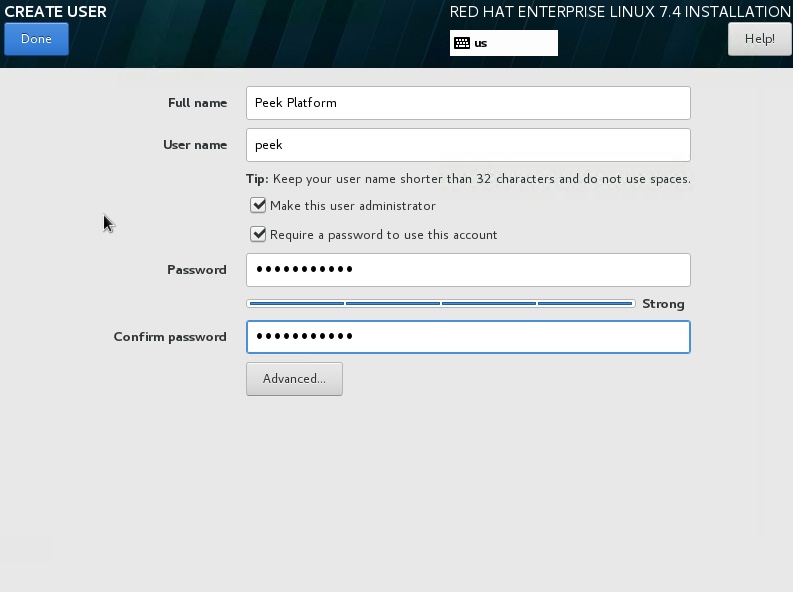
After the server has rebooted, deconfigure the RHEL ISO from DVD drive in the VM software.
The OS installtion is now complete.
Login as Peek¶
Login to the Debian VM as the peek user, either via SSH, or the graphical desktop if it’s
installed.
Important
All steps after this point assume you’re logged in as the peek user.
Configure Static IP (Optional)¶
If this is a production server, oit’s more than likely that you want to assign a static IP to the VM. Here is how you do this.
Note
Only do this is it wasn’t done during installation or requires updating. If you installed the GUI you can configure the static IP address with the GUI.
Edit file /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<device>
Update the following lines:
DEVICE=<device>
BOOTPROTO=none
ONBOOT=yes
HWADDR=<MAC_ADDRESS>
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
IPADDR=<IP_ADDRESS>
GATEWAY=<GATEWAY_ADDRESS>
TYPE=Ethernet
USERCTL=no
IPV6INIT=no
PEERDNS=yes
Installing General Prerequisites¶
This section installs the OS packages required.
Note
Run the commands in this step as the peek user.
To begin, make sure that all the packages currently installed on your RHEL/CentOS 7 system are updated to their latest versions:
sudo yum update -y
Install the C Compiler package, used for compiling python or VMWare tools, etc:
PKG="gcc gcc-c++ kernel-devel make"
sudo yum install $PKG
Install the Python build dependencies:
PKG="curl git m4 ruby texinfo bzip2-devel libcurl-devel"
PKG="$PKG expat-devel ncurses-libs zlib-devel libgmp-devel libssl-devel"
sudo yum install -y $PKG
Install C libraries that some python packages link to when they install:
PKG=""
# For the cryptography package
PKG="$PKG libffi-devel"
# For the python Samba client
PKG="$PKG samba-devel libsmbclient-devel"
sudo yum install -y $PKG
# For Shapely and GEOAlchemy
sudo yum install -y http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/g/geos-3.4.2-2.el7.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum install http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/g/geos-devel-3.4.2-2.el7.x86_64.rpm
# For LXML and the Oracle client
PKG="libxml2 libxml2-devel"
PKG="$PKG libxslt libxslt-devel"
PKG="$PKG libaio libaio-devel"
sudo yum install -y $PKG
# For the PostGresQL connector
sudo yum install -y http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/l/libpqxx-4.0.1-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum install -y http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/l/libpqxx-devel-4.0.1-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
# For the SQLite python connector
sudo yum install -y http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/l/libsqlite3x-20071018-20.el7.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum install -y http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/l/libsqlite3x-devel-20071018-20.el7.x86_64.rpm
Install rsync:
PKG="rsync unzip"
sudo yum install -y $PKG
Cleanup the downloaded packages:
sudo yum clean all
Installing VMWare Tools (Optional)¶
This section installs VMWare tools. The compiler tools have been installed from the section above.
In the VMWare software, find the option to install VMWare tools.
Mount and unzip the tools:
sudo rm -rf /tmp/vmware-*
sudo mount /dev/sr0 /mnt
sudo tar -xzf /mnt/VM*gz -C /tmp
sudo umount /mnt
Install the tools with the default options:
cd /tmp/vmware-tools-distrib
sudo ./vmware-install.pl -f -d
Cleanup the tools install:
sudo rm -rf /tmp/vmware-*
Reboot the virtual machine:
sudo shutdown -r now
Note
Keep in mind, that if the static IP is not set, the IP address of the VM may change, causing issues when reconnecting with SSH.
Compile and Install Python 3.6¶
The Peek Platform runs on Python. These instructions download, compile and install the latest version of Python.
Edit ~/.bashrc and insert the following after the first block comment.
Make sure these are before any lines like:
# If not running interactiviely, don't do anything
Insert:
##### SET THE PEEK ENVIRONMENT #####
# Setup the variables for PYTHON
export PEEK_PY_VER="3.6.5"
export PATH="/home/peek/cpython-${PEEK_PY_VER}/bin:$PATH"
# Set the variables for the platform release
# These are updated by the deploy script
export PEEK_ENV=""
[ -n "${PEEK_ENV}" ] && export PATH="${PEEK_ENV}/bin:$PATH"
Download and unarchive the supported version of Python:
cd ~
PEEK_PY_VER="3.6.5"
wget "https://www.python.org/ftp/python/${PEEK_PY_VER}/Python-${PEEK_PY_VER}.tgz"
tar xzf Python-${PEEK_PY_VER}.tgz
Configure the build:
cd Python-${PEEK_PY_VER}
./configure --prefix=/home/peek/cpython-${PEEK_PY_VER}/ --enable-optimizations
Make and Make install the software:
make install
Cleanup the download and build dir:
cd
rm -rf Python-${PEEK_PY_VER}*
Symlink the python3 commands so they are the only ones picked up by path:
cd /home/peek/cpython-${PEEK_PY_VER}/bin
ln -s pip3 pip
ln -s python3 python
Warning
Restart your terminal to get the new environment.
Test that the setup is working:
which python
echo "It should be /home/peek/cpython-3.6.5/bin/python"
which pip
echo "It should be /home/peek/cpython-3.6.5/bin/pip"
synerty-peek is deployed into python virtual environments. Install the virtualenv python package:
pip install virtualenv
The Wheel package is required for building platform and plugin releases:
pip install wheel
Install Worker Dependencies¶
Install the parallel processing queue we use for the peek-worker tasks.
Note
Run the commands in this step as the peek user.
Install redis:
mkdir /tmp/redis
cd /tmp/redis
# download redis dependencies
wget http://www6.atomicorp.com/channels/atomic/centos/7/x86_64/RPMS/jemalloc-3.6.0-1.el7.art.x86_64.rpm
# download redis
wget http://www6.atomicorp.com/channels/atomic/centos/7/x86_64/RPMS/redis-3.0.7-4.el7.art.x86_64.rpm
# install redis and dependencies
sudo yum install -y jemalloc-* redis-*
cd ~
rm -r /tmp/redis
Install rabbitmq:
# install erlang v20.3
sudo yum install -y https://github.com/rabbitmq/erlang-rpm/releases/download/v20.3.6/erlang-20.3.6-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm
# Set rabbitmq repository
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
# install rabbitmq
sudo yum install -y rabbitmq-server
Cleanup the downloaded packages:
sudo yum clean all
Enable the RabbitMQ management plugins:
sudo rm /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_mqtt
sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
sudo service rabbitmq-server restart
Install PostGreSQL¶
Install the relational database we use on Linux.
Note
Run the commands in this step as the peek user.
Install PostGreSQL:
sudo yum install -y postgresql-server postgresql-contrib
Create a new PostGreSQL database cluster:
sudo postgresql-setup initdb
Create the peek SQL user:
F="/var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf"
if ! sudo grep -q 'peek' $F; then
echo "host peek peek 127.0.0.1/32 trust" | sudo tee $F -a
fi
sudo systemctl start postgresql
sudo systemctl enable postgresql
sudo su - postgres
createuser -d -r -s peek
exit # exit postgres user
Create the database:
createdb -O peek peek
Set the database password:
psql <<EOF
\password
\q
EOF
# Set the password as "PASSWORD"
Cleanup traces of the password:
[ -e ~/.psql_history ] && rm ~/.psql_history
Install Oracle Client (Optional)¶
The oracle libraries are optional. Install them where the agent runs if you are going to interface with an oracle database.
Edit ~/.bashrc and insert the following after the first block comment.
Make sure these are before any lines like:
# If not running interactiviely, don't do anything
Insert:
# Setup the variables for ORACLE
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/home/peek/oracle/instantclient_12_2:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"
export ORACLE_HOME="/home/peek/oracle/instantclient_12_2"
Warning
Restart your terminal you get the new environment.
Make the directory where the oracle client will live
mkdir /home/peek/oracle
Download the following from oracle.
The version used in these instructions is 12.2.0.1.0.
- Download the ZIP “Instant Client Package - Basic” from http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/linuxx86-64soft-092277.html
- Download the ZIP “Instant Client Package - SDK” from http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/linuxx86-64soft-092277.html
Copy these files to /home/peek/oracle on the peek server.
Extract the files.
cd ~/oracle
unzip instantclient-sdk-linux.x64-12.2.0.1.0.zip
unzip instantclient-basic-linux.x64-12.2.0.1.0.zip
Symlink the oracle client lib
cd $ORACLE_HOME
ln -snf libclntsh.so.12.1 libclntsh.so
ls -l libclntsh.so
Install FreeTDS (Optional)¶
FreeTDS is an open source driver for the TDS protocol, this is the protocol used to talk to a MSSQL SQLServer database.
Peek needs this installed if it uses the pymssql python database driver, which depends on FreeTDS.
Edit ~/.bashrc and insert the following after the first block comment
Make sure these are before any lines like:
# If not running interactively, don't do anything
Insert :
# Setup the variables for FREE TDS
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="/home/peek/freetds:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH"
Warning
Restart your terminal you get the new environment.
Install FreeTDS:
sudo yum install http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/f/freetds-0.95.81-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum install http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/7/x86_64/Packages/f/freetds-devel-0.95.81-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
Create file freetds.conf in ~/freetds and populate with the following:
mkdir ~/freetds
cat > ~/freetds/freetds.conf <<EOF
[global]
port = 1433
instance = peek
tds version = 7.4
EOF
If you want to get more debug information, add the dump file line to the [global] section Keep in mind that the dump file takes a lot of space.
[global]
port = 1433
instance = peek
tds version = 7.4
dump file = /tmp/freetds.log
What Next?¶
Refer back to the How to Use Peek Documentation guide to see which document to follow next.